Learning Outcomes
i. Comprehend the purpose and functionality of the Task Manager in monitoring system performance and resource utilization
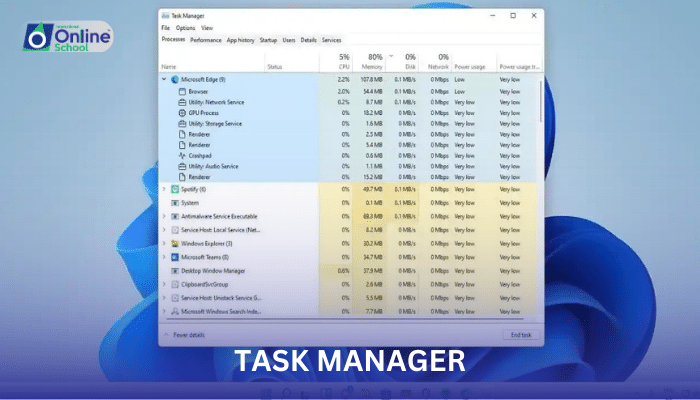
ii. Identify and interpret the information displayed in the Task Manager, including CPU, RAM, and disk usage
iii. Gain proficiency in monitoring system performance to identify potential bottlenecks and optimize resource usage
iv. Understand the process of terminating unresponsive applications to regain system responsiveness
v. Develop the ability to troubleshoot performance issues by analyzing Task Manager data
Introduction
In the dynamic realm of computer systems, the Task Manager emerges as a vigilant sentinel, providing real-time insights into the intricate dance of processes, resource allocation, and overall system performance. In this lesson, we delve into the depths of the Task Manager, empowering students to monitor system vitals, identify performance bottlenecks, and restore order when applications misbehave.
i. The Task Manager: Unveiling System Performance
The Task Manager serves as a command center, providing a comprehensive overview of system performance and resource utilization:
CPU Usage: Indicates the percentage of CPU resources consumed by running processes, enabling the identification of performance-hungry applications.
RAM Usage: Displays the amount of RAM (Random Access Memory) in use, revealing potential memory bottlenecks and resource constraints.
Disk Usage: Monitors the activity of hard disk drives or solid-state drives, indicating potential bottlenecks in data access and transfer.
ii. Monitoring System Performance to Identify Bottlenecks
Regular monitoring of system performance using the Task Manager allows users to:
Identify Performance Hogs: Pinpoint applications consuming excessive CPU resources, potentially impacting overall system responsiveness.
Detect Memory Leaks: Uncover applications that are not properly releasing RAM, leading to memory depletion and sluggish performance.
Monitor Disk Activity: Track disk usage patterns to optimize data access and prevent performance slowdowns caused by excessive disk activity.
iii. Terminating Unresponsive Applications
When applications freeze or become unresponsive, the Task Manager provides a means to restore system stability:
End Process: Terminates the unresponsive application, freeing up resources and restoring system responsiveness.
End Task Tree: Terminates the unresponsive application and all its child processes, ensuring a thorough cleanup.
Cautious Termination: Exercise caution when terminating processes, as some critical applications may cause system instability if terminated abruptly.
iv. Troubleshooting Performance Issues with Task Manager Analysis
The Task Manager serves as a valuable tool for troubleshooting performance issues:
Correlating Performance Issues with Resource Usage: Analyze spikes in CPU, RAM, or disk usage patterns to identify potential causes of performance degradation.
Identifying Misbehaving Applications: Pinpoint applications that are consistently consuming excessive resources or causing performance bottlenecks.
Seeking Expert Assistance: When complex performance issues arise, consult a trusted technical expert for in-depth analysis and resolution.
The Task Manager, a guardian of system performance, provides a comprehensive window into the inner workings of the computer system. By mastering the Task Manager's capabilities, students gain the ability to monitor resource usage, identify performance bottlenecks, troubleshoot unresponsive applications, and maintain a smoothly functioning computer system.